
This item may be available elsewhere in EconPapers: Search for items with the same title. 21 random sampling and latin hypercube sampling, although the latter leads. References: View references in EconPapers View complete reference list from CitEcĬitations: View citations in EconPapers (28) Track citations by RSS feedįull text for ScienceDirect subscribers only It is shown that these conclusions are true for both simple. It aims to generate samples of model inputs for investigating the sensitivity of their influence on.
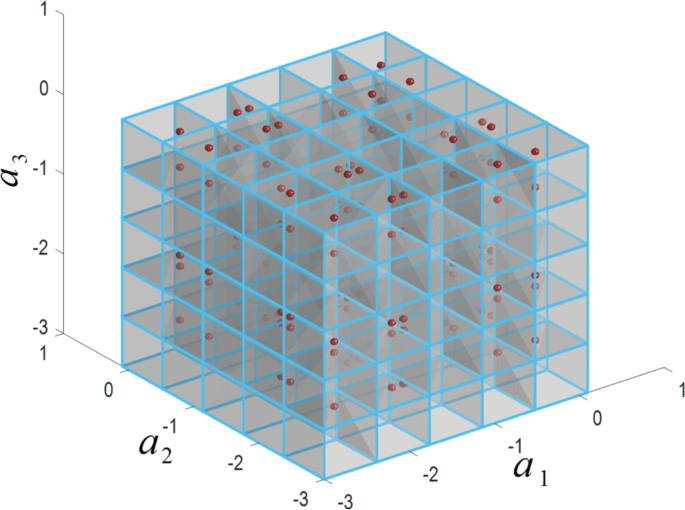
Keywords: Correlated parameters Latin hypercube sampling Linear regression Sensitivity analysis Uncertainty analysis (search for similar items in EconPapers) Latin hypercube sampling is a class of stratified Monte Carlo sampling methods without replacement, and was introduced by Mckay et al. Results show that the regression-based method can successfully measure the uncertainty contribution in the case where the relationship between response and parameters is approximately linear. The proposed regression-based method is then applied in three test cases. A square grid containing sample positions is a Latin square if and only if a single isolated sample exists in each row and each column 44. In this study, we propose a regression-based method to quantitatively decompose the total uncertainty in model output into partial variances contributed by the correlated variations and partial variances contributed by the uncorrelated variations. The Latin hypercube sampling defines a Latin square grid in an arbitrary number of dimensions where each sample is the lone sample in each axis-aligned hyperplane containing the sample 30. But these studies do not distinguish between the correlated and uncorrelated contribution of a parameter. So far, only a few studies have been conducted to obtain the sensitivity index for a model with correlated input. The parameters probability distribution (0 to 1) is divided into up to. the unique variations of a parameter which cannot be explained by any other parameters). The LHS option results in forced sampling from each stratum of each parameter. variations of a parameter which are correlated with other parameters) and the uncorrelated contribution (by the uncorrelated variations, i.e.

For models with correlated inputs, we propose that the contribution of uncertainty to model output by an individual parameter be divided into two parts: the correlated contribution (by the correlated variations, i.e. However, it is common that the parameters are correlated with each other. When conducting sensitivity and uncertainty analysis, most of the global sensitivity techniques assume parameter independence. Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 2008, vol. Uncertainty and sensitivity analysis for models with correlated parameters


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
